Insurance is ready for its AI moment
From claims processing to climate change, here's how AI could transform the modern insurance industry.
Insurance isn't the sexiest topic, but I must admit I find it inherently interesting. Maybe it’s because I’m German, where risk management —coupled with a long list of insurance policies — is woven into the fabric of our society.
Mostly, I view the insurance landscape opportunistically: The industry is data-heavy, full of repetitive tasks, and burdened by a pressing need to modernize. For most, it’s an industry stuck in time. For an investor in AI companies, it’s an open goal for innovation.
While I can’t claim deep insurance expertise, recent developments across other industries demonstrate how AI breathes new life into struggling sectors. I believe AI has the potential to reshape insurance by streamlining underwriting, automating claims, and uncovering new efficiencies. Whether it’s navigating the unpredictability of climate events, mitigating complex cyber risks, or adapting to advances in automation, AI positions insurers to act more nimbly and make smarter, data-driven decisions.
In insurance, this shift isn’t just about marginal improvements. It’s about rethinking how the industry functions from the ground up, offering enormous upside potential for those ready to tackle insurance’s existential problems with technology.
In this article I want to dive into a few ways I think insurance is ready for its AI moment. And of course, if you’re a founder building in this space, don’t hesitate to get in touch.
How AI Can Impact Insurance Businesses
Claims processing has barely changed in decades. Here’s what a typical process looks like:
Initial Reporting: The policyholder reports the incident and shares basic details.
Investigation: An adjuster verifies evidence and assigns liability.
Damage Assessment: A mechanic or appraiser estimates repair costs.
Approval and Payout: The insurer issues payment and closes the claim.
Multimodal AI, for instance, could streamline this entire workflow by processing text, images, and video simultaneously. This reduces hand-offs between departments, minimizes human error, and could save up to 75% in processing costs.
So, one clear avenue is to integrate AI into existing insurance systems such as claims processing, upgrading traditional workflows without a full “overhaul.”
The second, more radical path to build true “AI-native” insurance companies. There are a few such examples already.
The 9-year-old venture Lemonade, for instance, showcases this potential by integrating AI across its operations. The company reports issuing policies and processing claims in as little as two minutes, and has since rolled out policies for renters, homeowners, cars, pets and personal liabilities, as well as functioning as an agency for other insurance agencies. As of November 2024, Lemonade is valued at over $2bn and recently beat its Q3 earnings, sending shares soaring by over 30%.
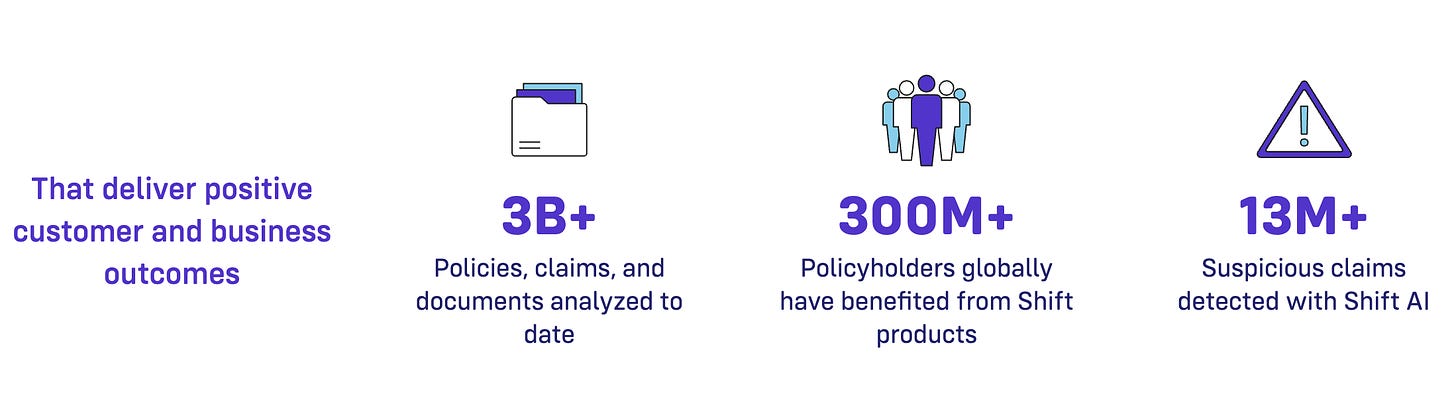
French unicorn Shift Technology offers another example of AI's influence on the industry. The company provides AI-driven tools for real-time fraud detection and automated claims handling, helping insurers reduce financial losses and enhance process efficiency. Shift’s systems analyze incoming claims to identify unusual patterns, which supports more informed underwriting and streamlines the claims process to boost customer satisfaction. The firm boasts over 100 customers, including Generali France and Mitsui Sumitomo, and reports to have analyzed nearly two billion claims, data that will only serve to improve its algorithms.
These two firms illustrate one of the industry’s biggest issues: legacy insurance companies had more data than they knew what to do with. This is where AI native companies will really pull ahead. Using APIs, these insurers can pull data from carriers, reinsurers, and other sources, instantly enabling custom underwriting and adaptive pricing. With the proliferation of connected devices - expected to reach up to a trillion by 2025 - AI will have even more data at its disposal to fuel personalized pricing, new product categories, and quicker service.
Using AI Insurtech to Tackle Humanity’s Existential Problems
The insurance industry doesn’t just need AI for efficiency—it needs it to stay resilient against new risks and growing demand from customers on contemporary challenges that are hard to price using traditional rails. Here’s why:
Climate
Extreme weather events are becoming more frequent, with over $1 trillion in damages recorded from more than 1,000 events in recent years. In 2022 alone, natural catastrophe claims surged by 54% compared to the previous 10-year average. This unpredictability makes it difficult for insurers to plan and price coverage effectively. Traditional models relying on historical data struggle as climate change destabilizes weather patterns, rendering past data less useful.
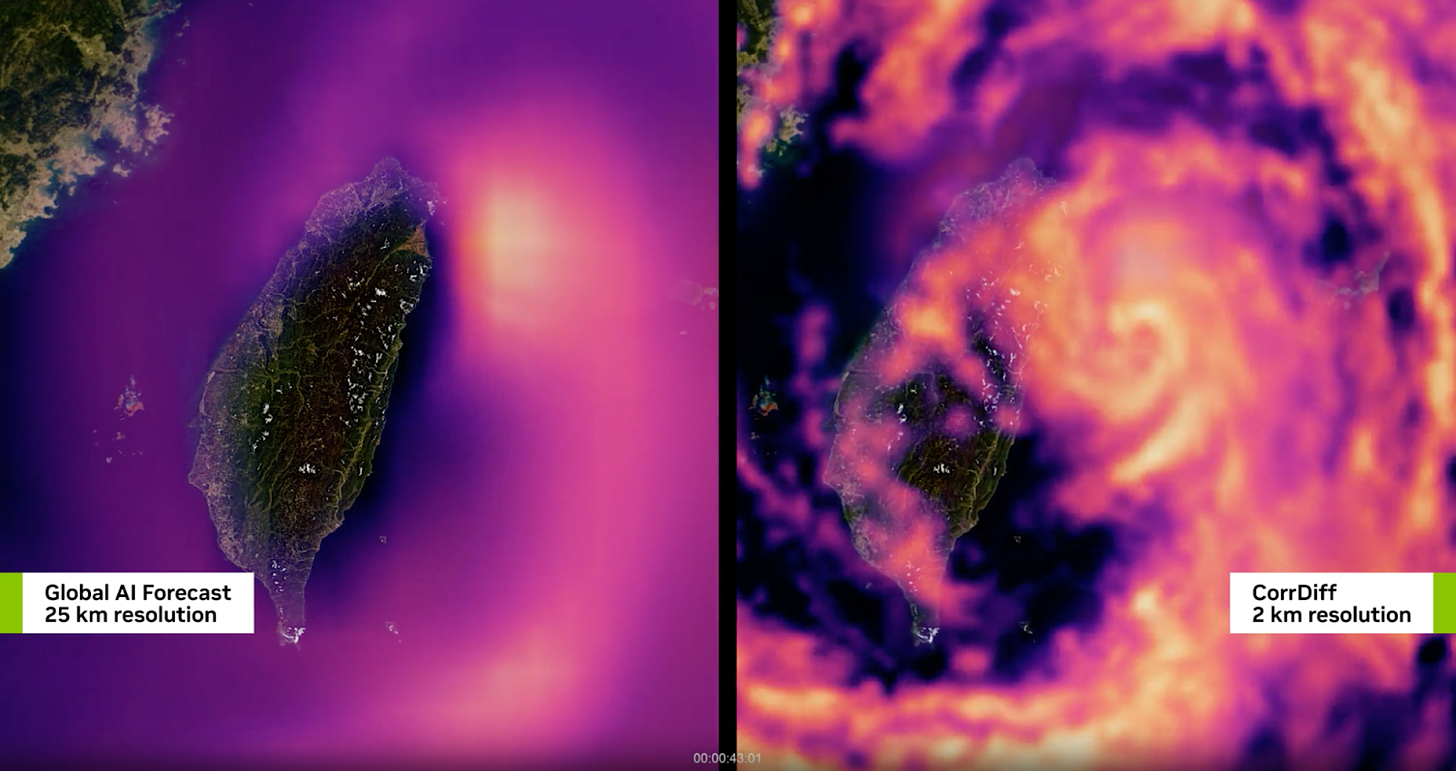
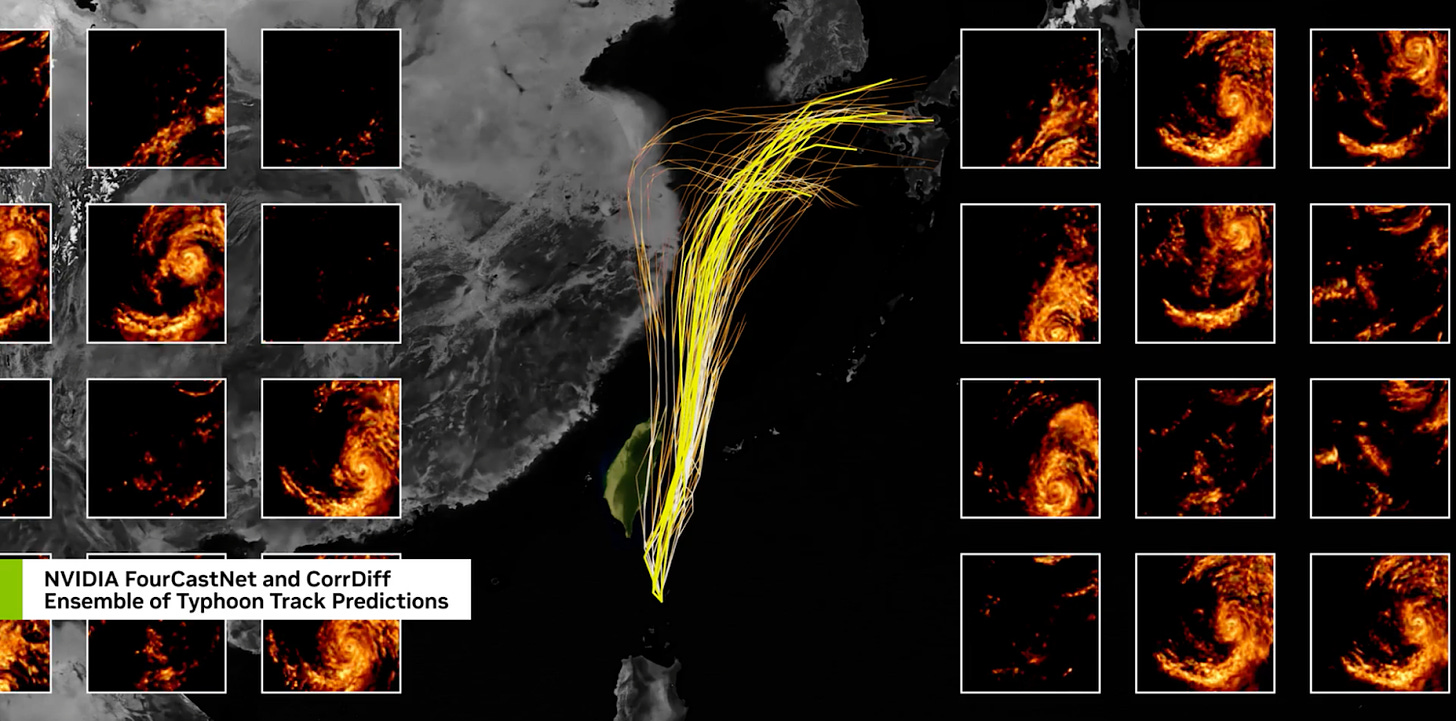
This is exactly the kind of situation where AI can shine. Let’s take the example of Taiwan, a country that is regularly battered by enormous storms. Traditional methods helped to mitigate the impact of extreme weather over time, but new AI models developed by NVIDIA have taken the predictive potential to the next level.
NVIDIA developed CorrDiff, a correlator diffusion model that can deliver a high resolution forecast for the entire globe in a fraction of the time needed by traditional models. CorrDiff has two steps: a regression model that predicts the mean of the fine-resolution field and a second step where it refines with the missing details that weren’t captured in the first prediction. NVIDIA trained the model on high-resolution, radar-incorporated WRF data from the Taiwan weather authorities and was able to predict extreme weather from 25km down to a 2km resolution.
Using advanced modeling, researchers achieved highly accurate storm simulations, enhancing both preparation and response. This is a potential game changer for insurers, as extreme weather scenarios change from educated guesswork to data-informed decisions that can be made in real time. Insurers can apply this precision to improve their pricing and reduce risks in regions prone to annual hurricanes and typhoons.
Tomorrow.io’s AI-driven weather intelligence provides another powerful example. The platform combines satellite data, ground sensors, and proprietary algorithms to deliver hyper-local forecasts, boosting accuracy by up to 80% over traditional models. A European insurer saved $12 million in claims within a year using this real-time intelligence to develop parametric insurance that triggers payouts based on predefined weather conditions, cutting down on administrative tasks and speeding up claim settlements by up to 25%.
Extreme weather is expected to get worse as the climate warms and areas that were previously safe will likely face growing environmental risk in future. Already, countries in areas that regularly face extreme weather are considered uninsurable. The need for modern, data-centric, parametric insurance solutions has never been higher and tools that cater to this have the potential to tap into a fast-growing market with urgent demand.
Cyber
Cyber incidents have become the top global business risk, with costs projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This has driven an urgent need for robust cyber insurance, and AI is uniquely positioned to offer solutions at various levels:
Prevention: AI-driven models can proactively identify vulnerabilities in company software, security setups, and network configurations, allowing insurers to make more precise risk assessments.
Detection: AI establishes real-time behavioral baselines, detecting anomalies early, even within IoT-connected devices, enhancing underwriting with improved real-time intelligence.
Response: Automated AI responses, like decoy environments, help isolate attackers and prevent data breaches, allowing human analysts to focus on complex threats and improving response speed.
Company Shield, a venture in our Merantix Capital portfolio, is working on the cutting edge of these issues from the vantage point of employee training, offering personalized simulation exercises of real-world AI attacks instead of boring long workshops and pro-forma “E-learning” training.
CyberCube is another example of how this potential can be transformed into a comprehensive business offering. The firm’s platform processes extensive datasets to analyze potential cyber threats, supporting insurers in making informed underwriting decisions and managing aggregated risk exposure. By embedding AI in their analytics, insurers can leverage predictive insights to anticipate vulnerabilities and refine their risk models. This helps improve the precision of underwriting, optimize pricing, and develop more resilient cyber insurance offerings.
Besides using AI to boost traditional cyber insurance options, the potential for AI in cyber insurtech actually gets kind of meta. Whole industries are in the process of integrating AI into their workflows. But AI-driven decision-making, something that Dimitris Bertsimas and Agni Orfanoudaki research in their 2021 Algorithmic Insurance report, comes with a whole new class of risk. In this sense, AI models are cyber products that require their own insurance policies. Let’s take a look at this in practice.
AI models are increasingly used to assist in detecting diseases as they are able to observe patterns and data that humans miss. The report presents a case study on breast cancer detection, illustrating how properties of the AI model, such as accuracy and interpretability, can influence the evaluation of insurance contracts.
The authors’ research suggested that the accuracy and interpretability of these models can directly influence the evaluation of insurance contracts. This is because the reliability of an AI system affects the potential risk exposure insurers take on when underwriting policies tied to AI outcomes. For instance, a highly accurate and transparent AI model may lower perceived risk and lead to more favorable contract terms, whereas a less reliable or opaque model could result in increased premiums or tighter policy conditions. This underscores the importance of assessing AI performance as it shapes liabilities in insurance products.
This shift means AI models themselves may need their own insurance frameworks, developed through quantitative analysis and supported by specialized insurtech models.
Armilla is one of the companies developing new AI risk assessments, including AI liability. Most AI-related risks do not fall under traditional cyber policies, creating a massive problem for the 70% of companies that McKinsey estimates will use AI by 2030. Targeting this market gap, the company is now an MGA focusing on AI insurance with capacity from Chaucer, Greenlight Re and Swiss Re.
Traditional insurers have frankly not been able to properly support companies implementing AI in their workflows. This is an urgent issue that will only get more pressing with time and the market is wide open for companies that can really get into the weeds of AI liability for an enormous, global market.
Robotics in the Workplace
From factories staffed by autonomous devices to humans toiling alongside machines on assembly lines, robots are already pretty common in the workplace.
VIDEO: Amazon showcases 1st fully autonomous mobile warehouse robot
But what happens when a machine powered by an AI algorithm hurts someone. Can you sue the robot? The factory owner? Or the developer that designed the algorithm? These are things that insurance companies will have to think about quite urgently, considering that up to 25% of manufacturing tasks are expected to be automated by robots in the next few years.
According to a Lloyd’s research report, collaborative robots, known as “cobots” introduce new risks to the workplace, from potential injuries from unexpected movements to cybersecurity, operational failures and compliance issues.
AI-powered monitoring systems enable insurers to continuously oversee robotic systems, detecting anomalies that could signal malfunctions. This proactive approach is critical in sectors like manufacturing and healthcare, where equipment failures can lead to significant costs or even physical harm. AI-driven sensors and real-time data analysis allow insurers to assess risks dynamically, improving both the precision and adaptability of coverage.
As it stands, few insurance companies are in a position to handle the data required to monitor such new risks, or be able to adapt policies to them in real time. Robotics is a fast-moving and rapidly growing industry, but one lawsuit at the wrong time could easily shutter businesses.
Now is the time for ambitious founders to step forward and create nimble, comprehensive insurance solutions that will protect companies, their employees and the innovation they are seeking to bring into the sector.
The Future of Insurance
The insurance industry is ripe for transformation through artificial intelligence. This shift isn’t just about turning around a sector bogged down by legacy systems, it’s a chance for mission-driven founders to tackle pressing global challenges, make a tangible impact, and attract significant funding.
Climate change is an unfortunate reality, with increasingly unpredictable weather events demanding urgent solutions. AI finally empowers insurers to make real-time, data-informed decisions that mitigate risks and enhance response strategies. Similarly, the rise of AI has brought new cyber vulnerabilities, requiring tailored insurance solutions to cover emerging threats and even AI products themselves.
Robotics, a frontier signaling the future of work and industry, introduces specific risks that most insurtechs are not yet prepared to address. Founders with expertise in automation, data, and insurance have a unique opportunity to lead in shaping solutions that meet these challenges.
Traditional insurance might be fighting off obsolescence. But for agile companies leveraging AI, there has never been a better time to be in the industry. I’m excited to see (and help build and invest in) this next frontier in insurance.